AWS
AWS Cloud Security Assessment Project
Cloud Security

AWS Cloud Security Assessment Project
- The objective of this project was to demonstrate how to identify and remediate security issues in an AWS environment using a running EC2 instance. I used AWS Inspector, Security Hub, Config, and GuardDuty to detect vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and missing security controls.
- This project taught me how to evaluate findings, prioritize risks, and apply fixes effectively. For example, I identified exposed services through a public IP address, which could allow brute-force attacks against SSH, RDP, or SQL services. I also confirmed the importance of MFA, IAM credential protection, and proper password policies to prevent unauthorized access.
- I remediated issues by updating vulnerable packages (e.g., GRUB2 and Vim), enabling CloudTrail logging, configuring detailed EC2 monitoring, and enforcing IAM password complexity requirements. These changes reduced the attack surface, improved visibility, and strengthened the overall security posture of the environment.
- Below is a detailed breakdown of the vulnerabilities, prioritization decisions, and remediation steps:
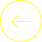
 B) Prioritization – why these first?
This CVE should be prioritized due to:
B) Prioritization – why these first?
This CVE should be prioritized due to:
- Secure Boot Bypass Risk – Attackers could exploit this to disable boot protections, leading to system compromise.
- Widespread Exposure – Systems using GRUB2 (Amazon Linux, Ubuntu, Red Hat, etc.) are vulnerable.
- Potential Remote Exploitation – If an attacker modifies boot parameters remotely, this vulnerability could enable persistent access.
- Amazon Linux 2023 & Other Linux-Based EC2 Instances – If not patched, secure boot mechanisms could be bypassed, increasing persistence risks.
- Hypervisors & Virtual Machines – Systems running GRUB2 could be exploited to alter boot sequences, enabling deeper infiltration.
- Bootloader Security – Could undermine trust in cryptographic validation, potentially leading to kernel tampering.
- Low to Moderate for standard updates – Amazon Linux provides patched versions of grub2-common and grub2-efi-x64-ec2.
- Moderate to High for custom implementations – If using custom GRUB2 configurations, manual recompilation may be needed.
- Verification Required – Post-update scans with AWS Inspector or manual checks should confirm mitigation.
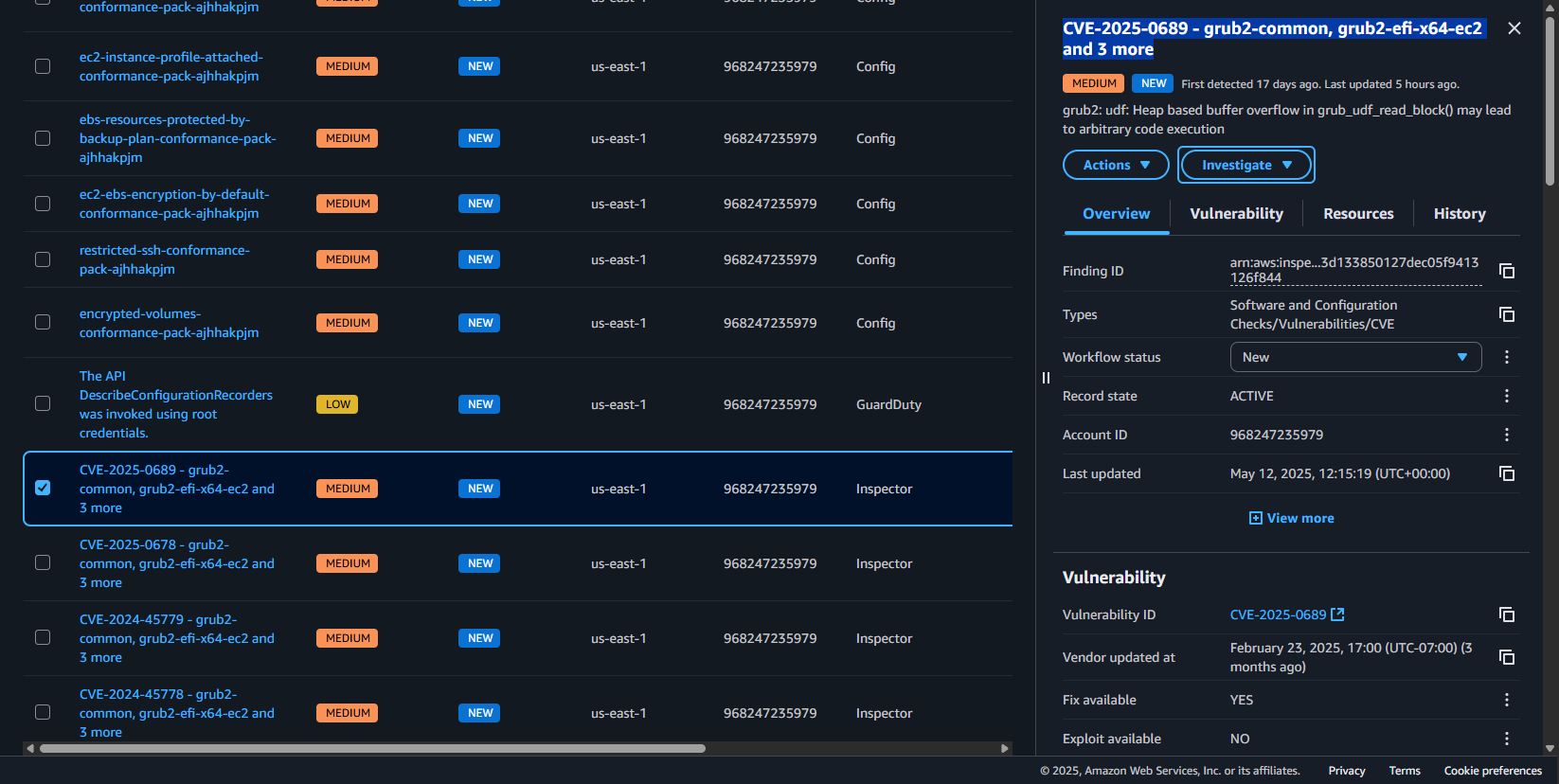
- Update GRUB2 Immediately:
- Reinstall Bootloader:
- (Replace /dev/sdX with the correct boot disk.)
- Verify Fix with AWS Inspector – Scan EC2 instances to confirm mitigation.
- Monitor Amazon Linux Security Advisories for additional updates.
 D) Vulnerability completed and Fixed
D) Vulnerability completed and Fixed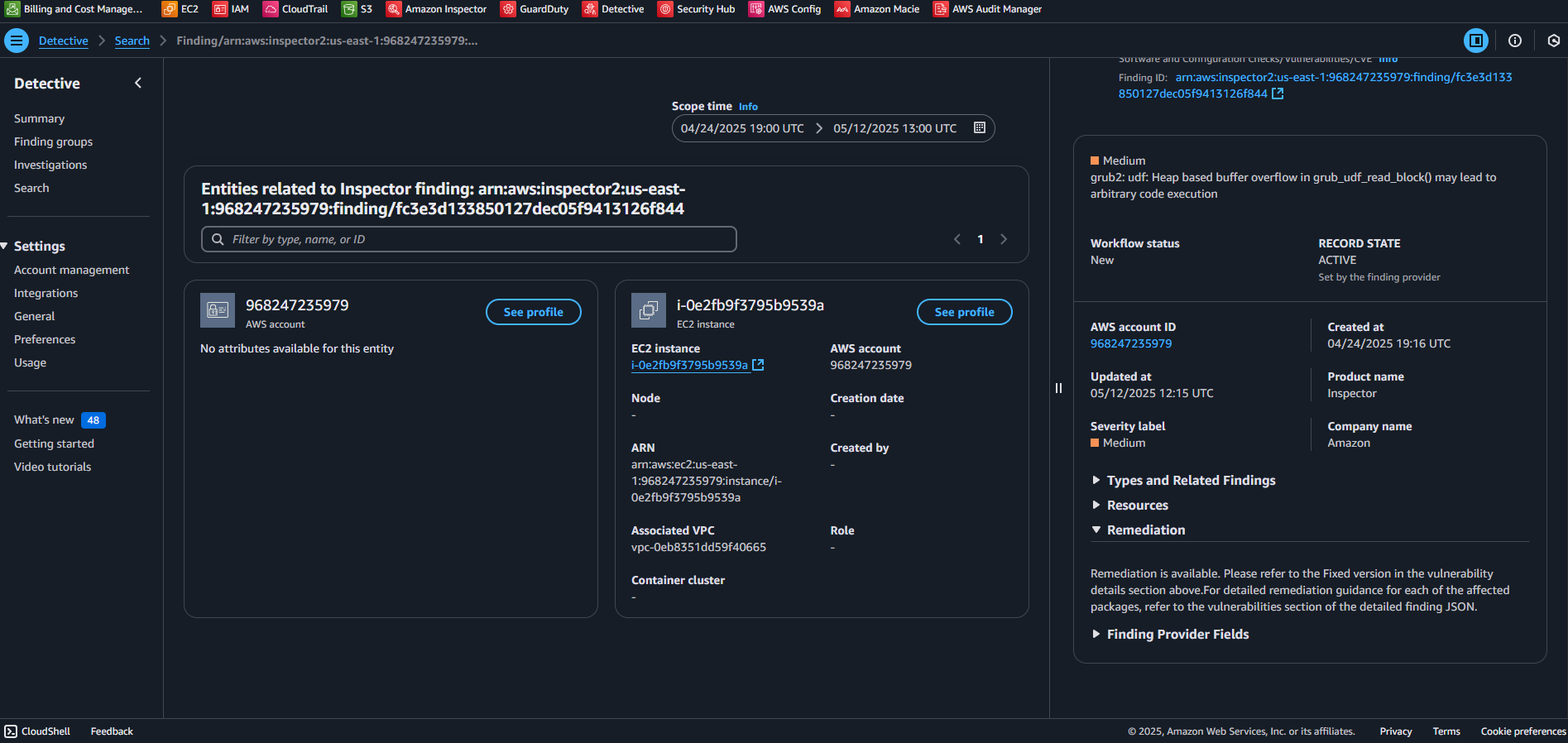 A) CVE-2025-26603-vim-common, vim-data and 4 more
A) CVE-2025-26603-vim-common, vim-data and 4 more
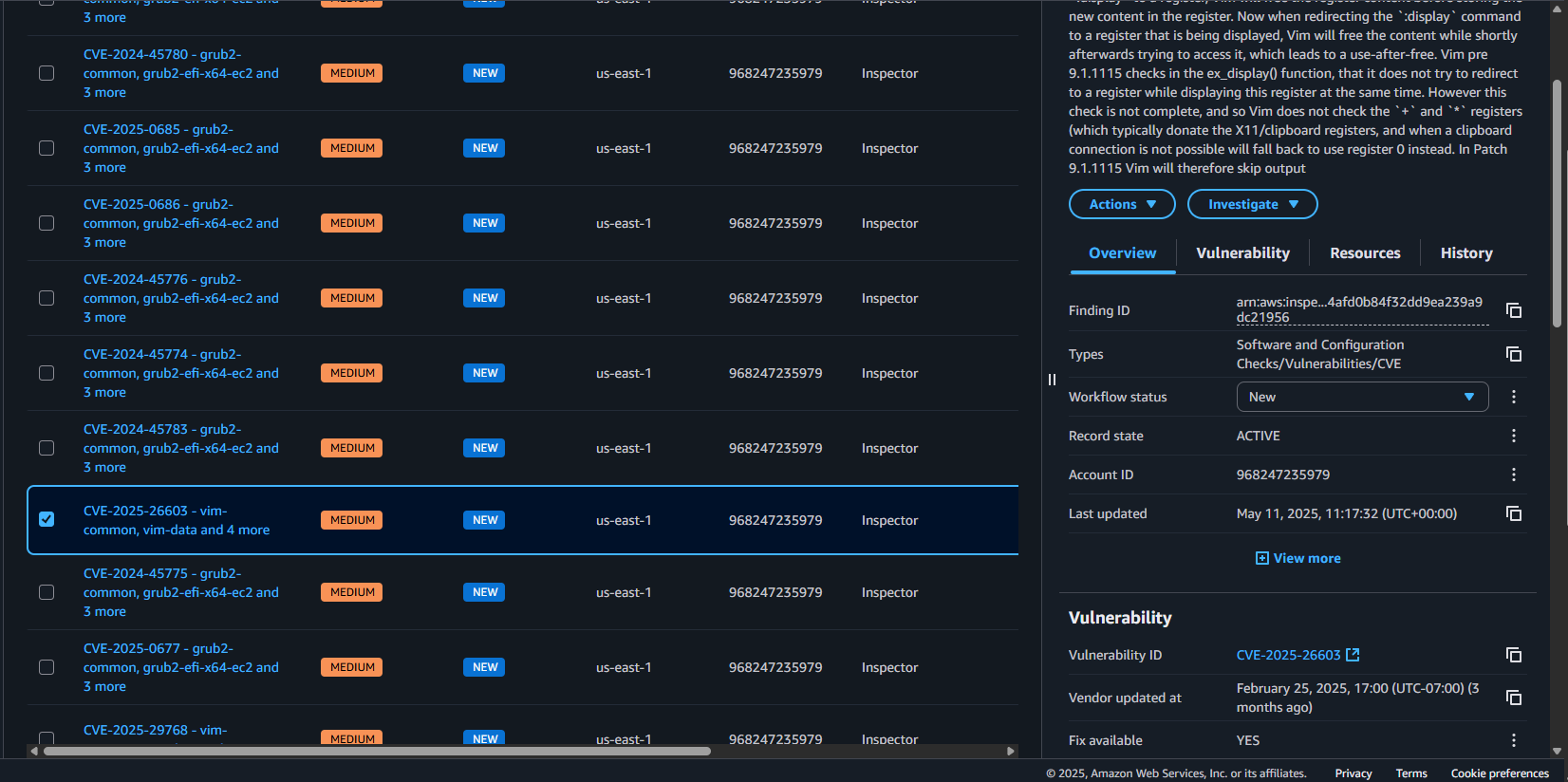 Prioritization – why this one first?
CVE-2025-26603 should be addressed promptly due to:
Prioritization – why this one first?
CVE-2025-26603 should be addressed promptly due to:
- Potential for Remote Code Execution – Exploiting Vim’s vulnerability could enable an attacker to execute arbitrary commands with elevated privileges.
- High-Risk Applications – Many AWS workloads rely on Vim for configuration and scripting, making widespread exposure possible.
- User Interaction-Based Exploits – The vulnerability can be exploited when opening malicious files or interacting with specific Vim commands, posing risks in operational environments.
- Amazon Linux 2 & 2023 EC2 Instances – Systems using Vim for editing configurations may be exposed.
- Containerized Workloads – If Vim is bundled into Docker containers, unpatched versions could persist.
- Automation Scripts & CI/CD Pipelines – Vulnerable Vim installations could pose risks in environments that rely on script execution for deployment.
- Low – If running standard Amazon Linux versions, updating Vim is straightforward with “dnf” or “yum”.
- Moderate – If Vim is used in custom-built containers or scripts, updates may require image rebuilds and testing.
- Verification Required – AWS Inspector or manual checks should confirm the vulnerability is mitigated post-update.
- (Amazon Linux 2 users should use yum instead.)
- Verify Fix with AWS Inspector – Scan EC2 instances to confirm mitigation.
- Check for Vulnerable Containers – Ensure Vim versions inside Docker containers are updated.
- Restrict Untrusted Vim Scripts – Apply controls to prevent execution of unverified “.vimrc” files and macros.
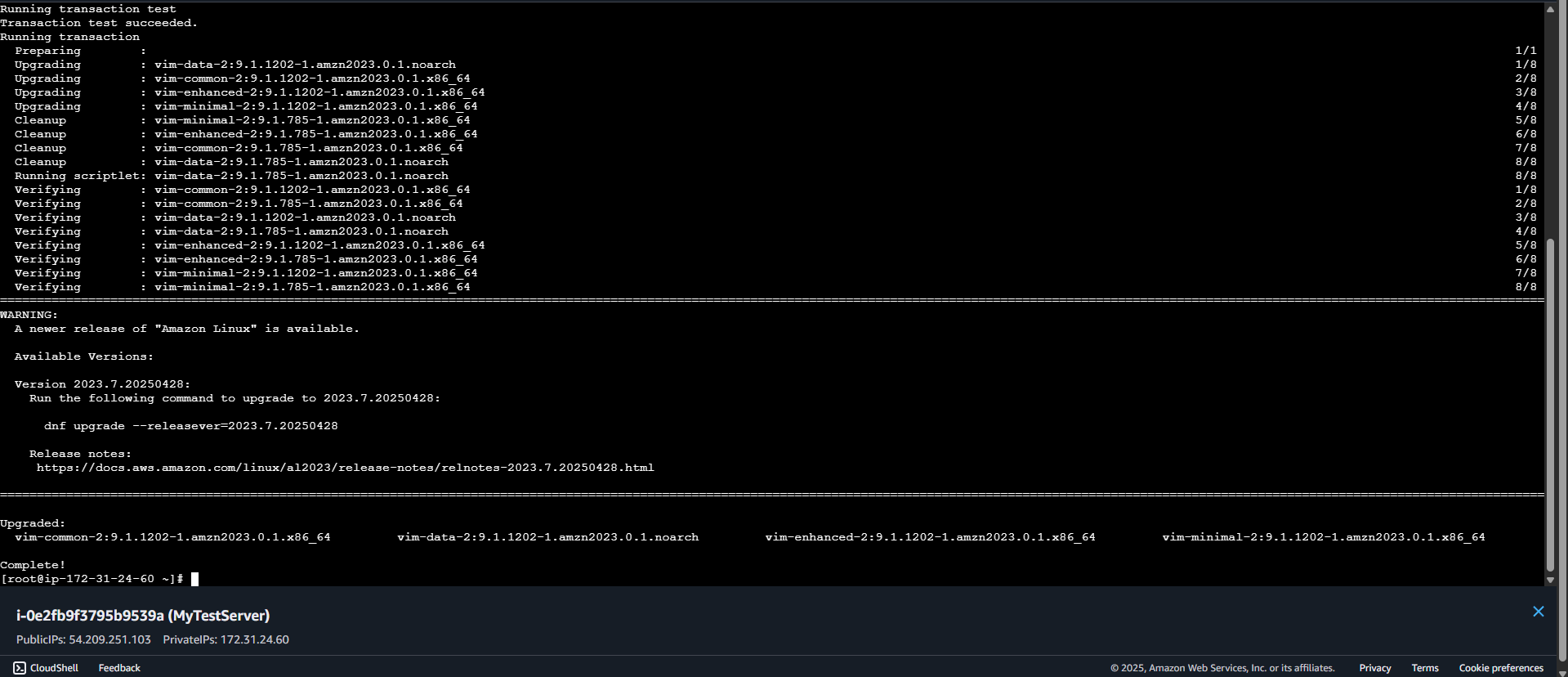 D) Vulnerability fixed and showing it complete
D) Vulnerability fixed and showing it complete  2: AWS Config
2: AWS Config
- cloudtrail-s3-dataevents-enabled-conformance-pack-ly8zmmii3
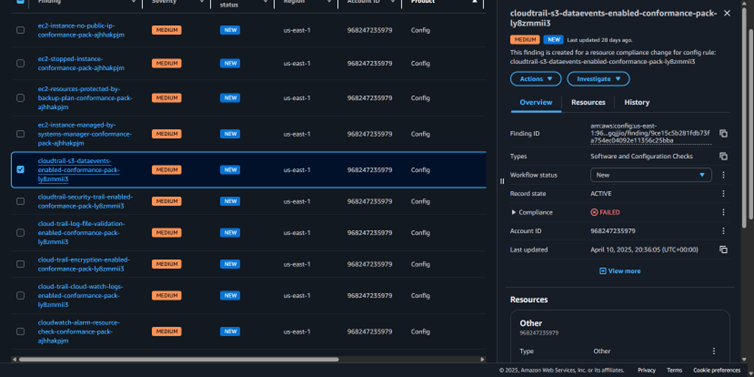 Prioritization – why this one first?
Prioritization – why this one first?
- Critical Data Visibility – CloudTrail logs data events for S3, ensuring detailed auditing of access and modifications.
- Prevent Unauthorized Data Access – Potential data exfiltration or unauthorized changes can go unnoticed without monitoring.
- Regulatory Compliance – Many standards (CIS, NIST, GDPR, PCI DSS) require logging data access events to secure sensitive information.
- S3 Buckets – No visibility into who accessed or modified data, increasing security risks.
- Security & Compliance Frameworks – A Lack of logs may cause non-compliance with governance requirements.
- Incident Response & Forensics – Security teams cannot investigate breaches effectively without logs.
- Low Effort – Enabling S3 data event logging in CloudTrail is a one-step configuration.
- Minimal Impact – Logs are stored in S3 and CloudWatch, requiring no additional infrastructure.
- Ongoing Monitoring Needed – Regular log analysis is required to detect anomalies.
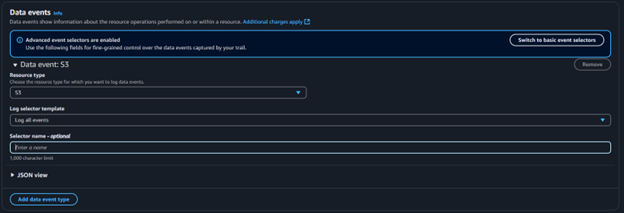
- Enable CloudTrail S3 Data Event Logging
-
- Open AWS CloudTrail Console → Select your active trail.
-
- Click Event Selector → Enable S3 Data Events → Choose "All Buckets" or specify targets.
- Store Logs in an Encrypted S3 Bucket
-
- Ensure log integrity validation is enabled.
-
- Apply SSE-KMS encryption to secure CloudTrail logs.
- Set Up Alerts for Anomalies
-
- Create CloudWatch Alarms for unusual S3 data access patterns.
-
- Use Amazon SNS Notifications for security teams.
- Verify Compliance in AWS Security Hub
- Check findings related to CloudTrail logging gaps.
- Run AWS Config scans to confirm logging is enabled.
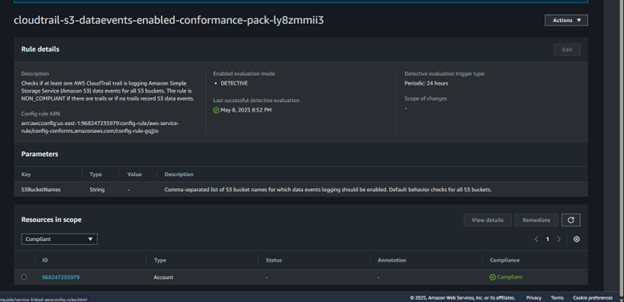
 D) Shown below is the vulnerability being compliant after fixing
D) Shown below is the vulnerability being compliant after fixing
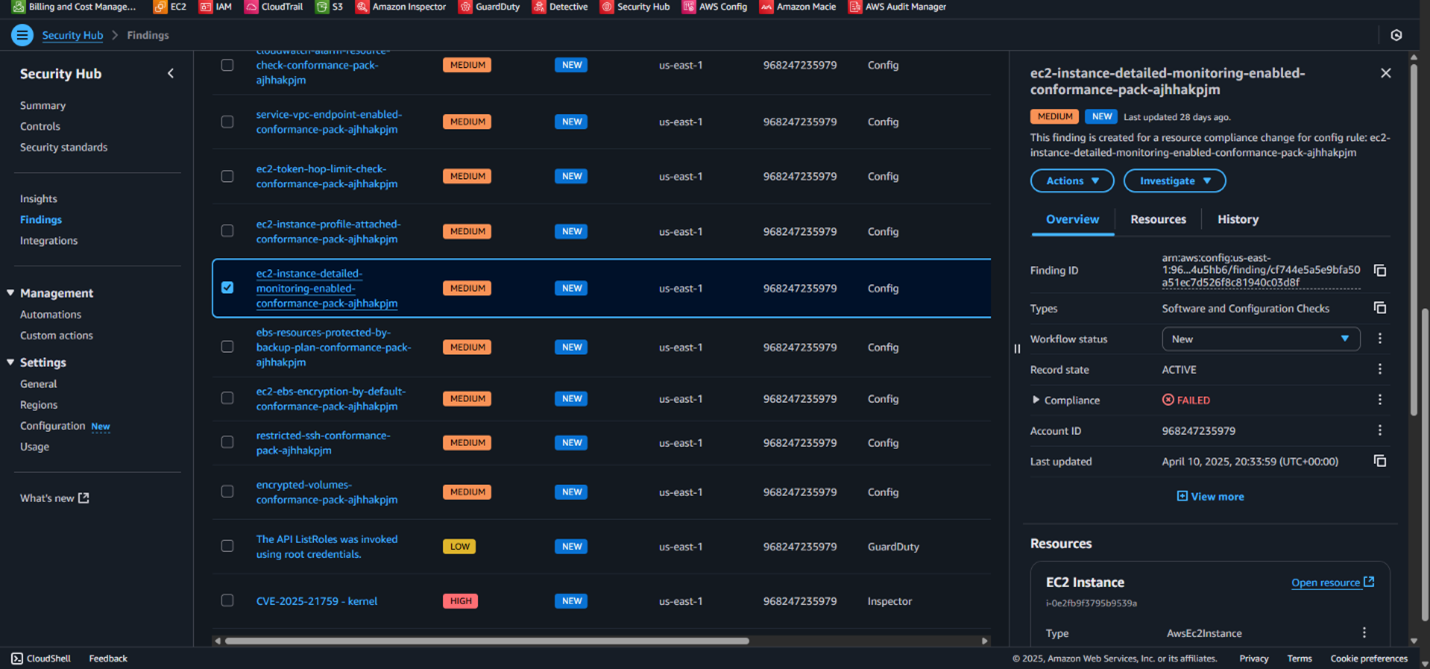
 A) ec2-instance-detailed-monitoring-enabled-conformance-pack
A) ec2-instance-detailed-monitoring-enabled-conformance-pack
 Prioritization – why this one first?
Prioritization – why this one first?
- Improved Performance Visibility – Enables real-time metrics for CPU utilization, disk I/O, and network traffic.
- Faster Issue Detection – Helps pinpoint performance bottlenecks and anomalies quickly.
- Recommended for Mission-Critical Workloads – Essential for maintaining availability and optimizing resource usage.
- EC2 Instances – Limited visibility into real-time performance data, making troubleshooting harder.
- CloudWatch Metrics – AWS only provides basic metrics every five minutes without detailed monitoring, reducing incident response speed.
- Auto Scaling & Cost Optimization – Inefficient scaling decisions due to incomplete performance data.
- Low Effort – Enabling detailed monitoring is a simple toggle within EC2 settings.
- Minimal Impact – Does not require application changes but slightly increases CloudWatch costs.
- Ongoing Maintenance – Metrics must be monitored proactively to take full advantage.
- Enable Detailed Monitoring in EC2
-
- Open AWS EC2 Console → Select the instance.
-
- Click Modify Instance Settings → Check Enable Detailed Monitoring.
- Configure CloudWatch Alarms for Critical Metrics
-
- Set up alarms for CPU utilization, network traffic, and disk I/O spikes.
-
- Use SNS notifications to alert security teams.
- Integrate with AWS Cost Management
-
- Review CloudWatch usage to ensure cost efficiency.
-
- Optimize instance types based on performance trends.
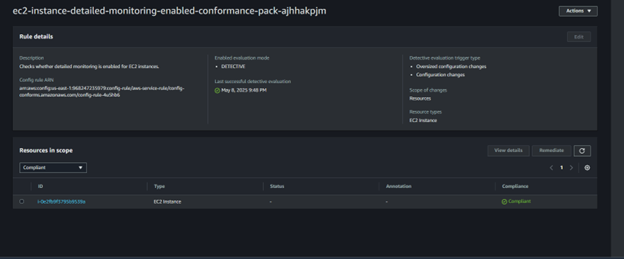
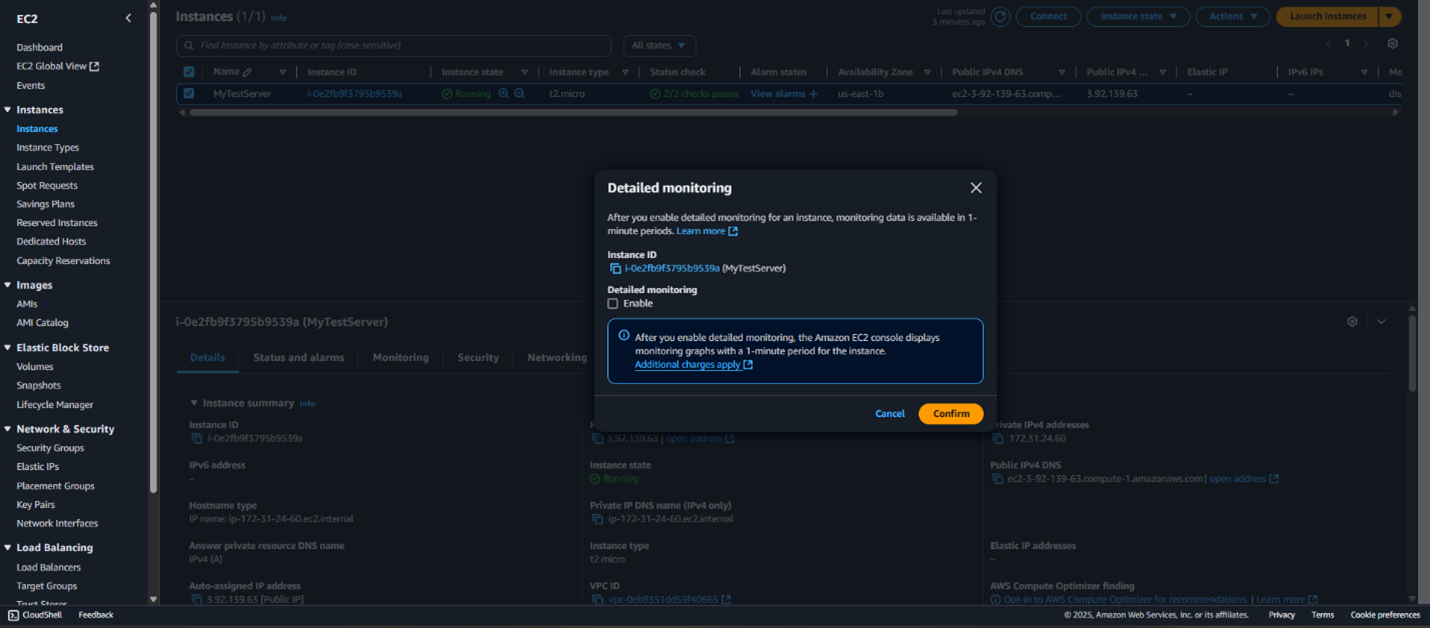 D) Vulnerability showing its now compliant and fixed
D) Vulnerability showing its now compliant and fixed
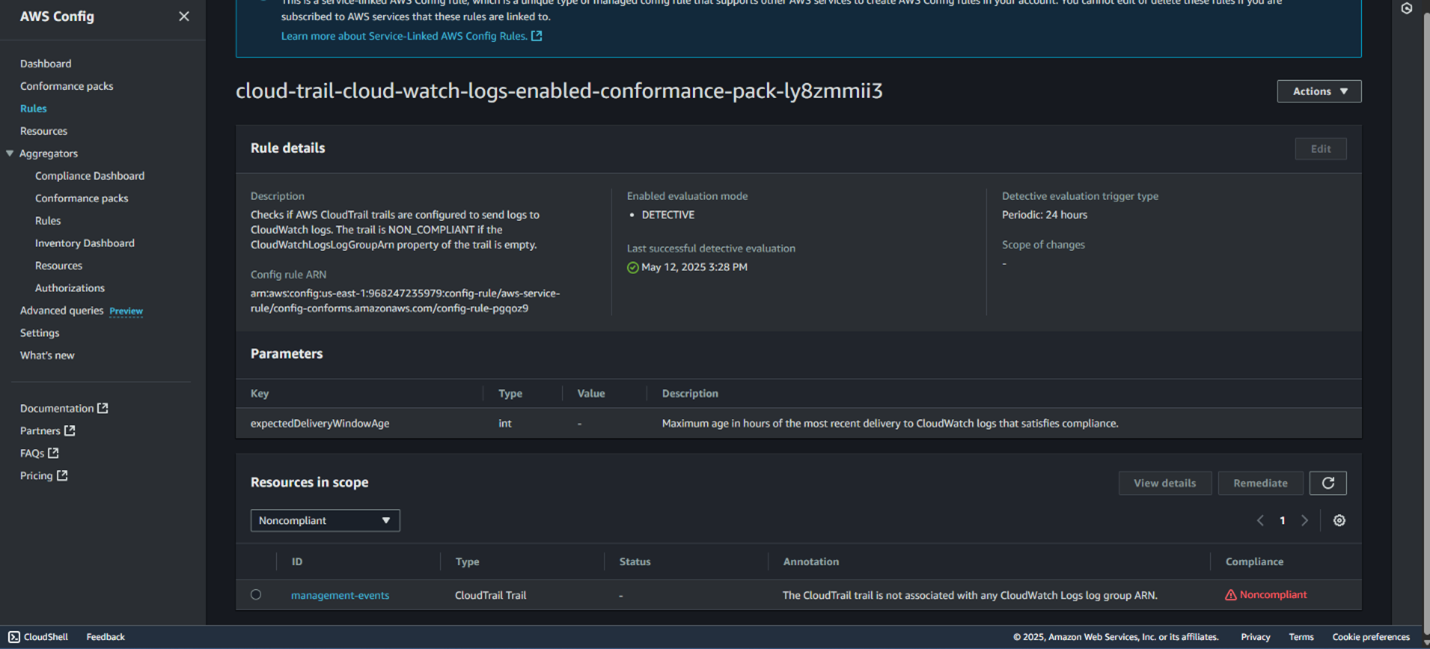
 A) Cloud-trail-cloud-watch-logs-enabled-conformance-pack-Ly8Zmmii3
A) Cloud-trail-cloud-watch-logs-enabled-conformance-pack-Ly8Zmmii3
 B) Prioritization – Why This One First?
B) Prioritization – Why This One First?
- Critical for Security Monitoring – CloudTrail logs track AWS API activity, and sending logs to CloudWatch enables real-time Monitoring.
- Incident Response Readiness – Without CloudWatch integration, detecting suspicious activity becomes delayed, increasing security risks.
- Compliance Requirement – Many security frameworks (CIS, NIST, PCI DSS) mandate log retention and Monitoring to ensure security visibility.
- IAM & User Activity Logs – Unauthorized access attempts may go unnoticed.
- EC2, S3, and Other AWS Services – Reduced visibility into configuration changes, API calls, and resource modifications.
- Security Operations & Forensic Analysis – Delays in threat detection and difficulty in investigating security incidents.
- Low Effort – Enabling CloudTrail log delivery to CloudWatch is a straightforward configuration update in the AWS Console.
- Minimal Performance Impact – It does not require new infrastructure but may slightly increase CloudWatch costs for log storage.
- Ongoing Monitoring Required – Regular log analysis ensures compliance and helps detect security issues proactively.
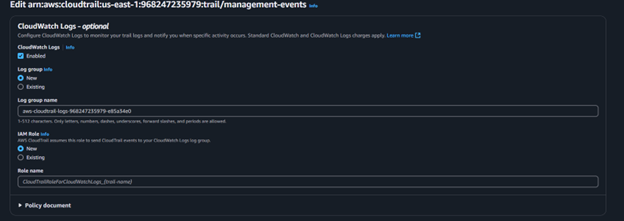
- Enable CloudTrail Logging to CloudWatch
-
- Open AWS CloudTrail Console → Select the existing trail.
-
- Click Edit → Enable CloudWatch Logs Integration.
-
- Choose an existing CloudWatch Log Group or create a new one.
- Assign Permissions Using IAM Role
-
- Create an IAM role that allows CloudTrail to write logs to CloudWatch.
-
- Attach the required permissions (CloudWatch Logs Write Access).
- Set Up CloudWatch Alerts for Security Monitoring
-
- Create Metric Filters to detect critical security events.
-
- Configure CloudWatch Alarms and link them to an SNS topic to notify security teams.
- Verify Compliance & Continuous Monitoring
-
- Run an AWS Config Compliance Scan.
-
- Check AWS Security Hub for any CloudTrail logging violations.
-
- Regularly audit CloudWatch logs for anomalies.
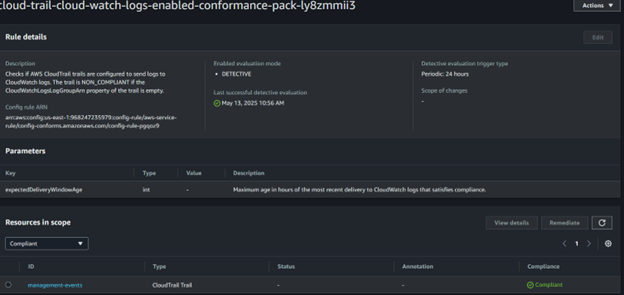
 D) Vulnerability showing being compliant and fixed
D) Vulnerability showing being compliant and fixed
 4: AWS Security Hub
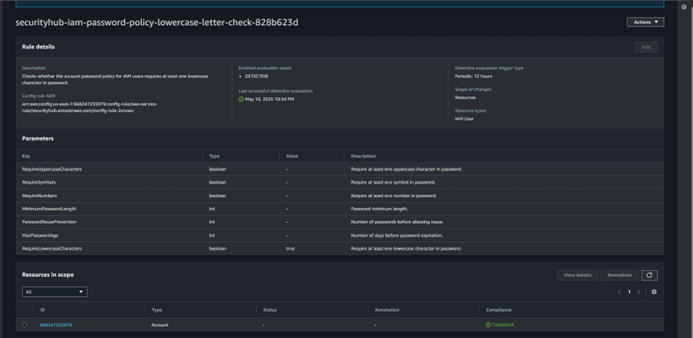
A) Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one lowercase letter
4: AWS Security Hub
A) Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one lowercase letter
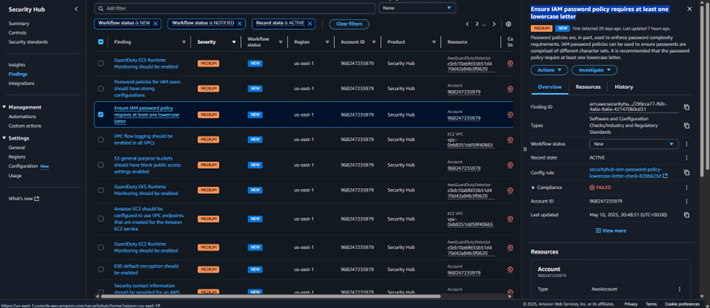 B) prioritization – why this one first?
B) prioritization – why this one first?
- Strengthens Authentication Security – Enforcing a complex password structure reduces the risk of brute-force attacks.
- Common Password Weakness – Many users create passwords with predictable patterns, increasing vulnerability.
- Regulatory Compliance – Security frameworks (CIS, NIST, ISO 27001) mandate strong password policies to protect access credentials.
- IAM User Accounts – Weak passwords make accounts easier to compromise.
- AWS Management Console & API Access – Attackers could gain unauthorized access to AWS resources.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) & Identity Protection – Even with MFA, a weak password increases the risk of credential stuffing attacks.
- Low Effort – Updating the IAM password policy is a quick configuration change in AWS IAM settings.
- Minimal Operational Impact – No downtime, but existing users may need to update their passwords.
- Ongoing Monitoring Required – Regular audits ensure compliance and detect weak password usage
- Update IAM Password Policy
- Open AWS IAM Console → Navigate to Account Settings.
- Click Set Password Policy → Enable Require at Least One Lowercase Letter.
- Apply the changes and enforce policy updates for all users.
- Educate Users on Secure Password Practices
- Recommend using password managers to generate strong, compliant passwords.
- Encourage users to follow NIST guidelines for passphrase-based authentication.
- Enable AWS Config Rule for Password Policy Compliance
- Open AWS Config Console → Create a rule for IAM Password Policy Validation.
- Set alerts for non-compliant password configurations.
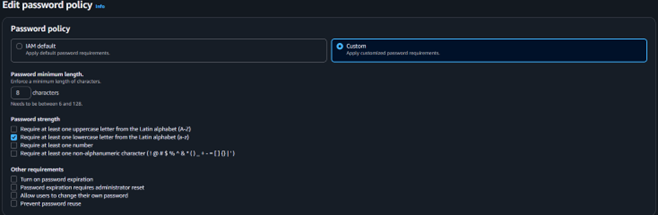 D) Vulnerability showing that it is now Compliant and fixed
D) Vulnerability showing that it is now Compliant and fixed